Here are the main technical specifications you should look at when picking a 35kV Oil-immersed Transformer:
Specification | Typical Value |
Rated Voltage | 35kV |
Capacity Range | 50–5000 kVA |
Frequency | 50Hz/60Hz |
Insulation Class | High-grade materials |
Cooling Type | Oil-immersed |
Voltage Regulation | NLTC (No Load Tap Changer) |
You need to think about these things because insulation quality, oil type, and cooling methods can change how safe, reliable, and long-lasting the transformer is. Testing the oil often and making sure the load is right help stop problems and keep your transformer working well.
Pick a transformer with strong insulation for safety and long life. Good insulation lowers repair costs and helps it work better.
Test the transformer oil often to keep it in good shape. This stops breakdowns and helps the transformer last longer.
Choose a transformer with low no-load and load losses. This saves energy and lowers how much it costs to run.
Think about cooling methods like ONAN and ONAF for best results. Good cooling stops overheating and makes the transformer more reliable.
Make sure the transformer meets all needed standards and certifications. This keeps the transformer safe and working well.
Insulation and Oil
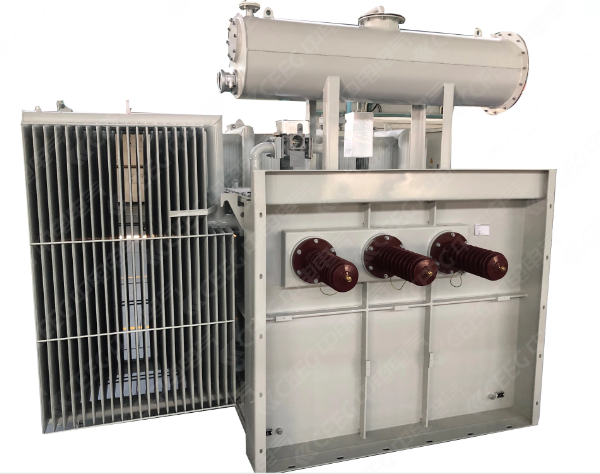

Insulation Materials and Classes
Insulation is very important for the safety of a 35kV Oil-immersed Transformer. Manufacturers use strong materials like high-temperature paper and Nomex®. These help the transformer work with high voltages and hard conditions. Insulation class ratings tell you how much heat the insulation can take before it fails. The table below shows different insulation classes and their top temperatures:
Insulation Class | Maximum Operating Temperature (°C) |
A | 105 |
F (epoxy resin) | 155 |
H | 180 |
C | 220 |
You can look at the chart below to compare these classes:
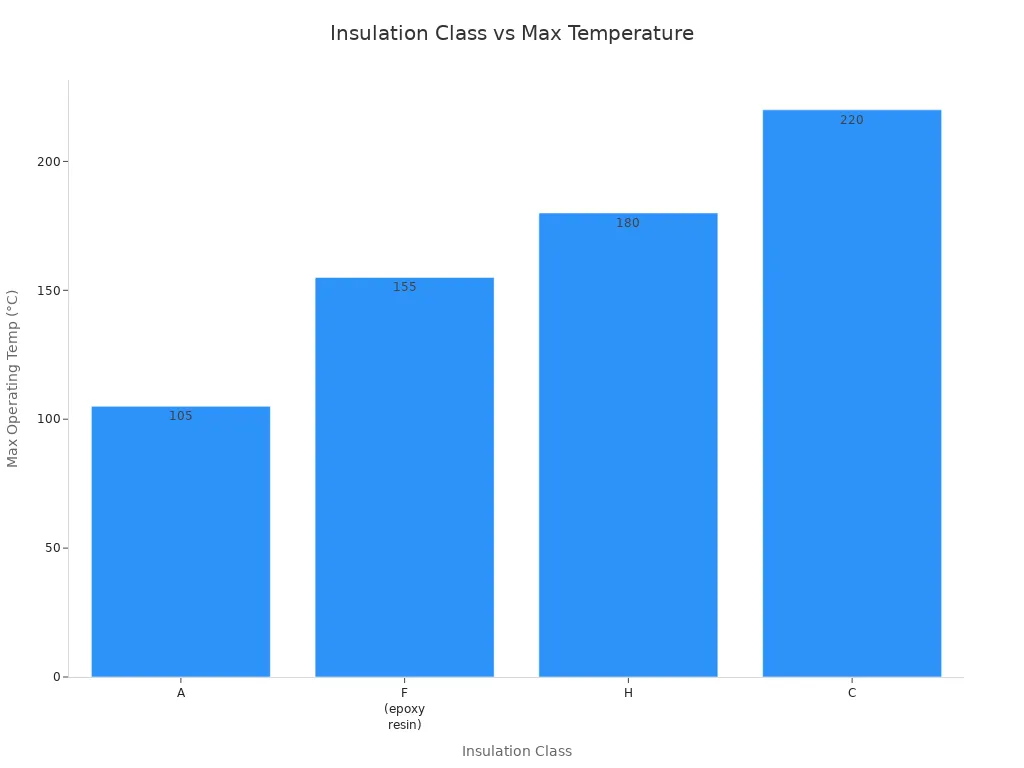
Good insulation helps your transformer last longer. It also lowers repair costs and slows down aging. High-temperature insulation lets your transformer work well in tough places.
Dielectric Strength and Testing
Dielectric strength shows how well the insulation and oil stop electrical breakdown. You should test this often to keep your 35kV Oil-immersed Transformer safe and working right. Some common tests are:
Voltage Test: Finds the lowest voltage where the oil breaks down.
Dielectric Loss Test: Checks how much power is lost in the insulation.
Simplified Test: Looks at simple things like acidity and pH.
Testing steps include getting the oil sample ready, putting in electrodes, turning on voltage, and writing down results. Regular testing helps you find problems early, like water or dirt, which can hurt insulation and make the transformer not last as long.
Transformer Oil Types and Properties
Transformer oil cools and insulates your 35kV Oil-immersed Transformer. The most used oils are naphthenic and paraffinic mineral oils. The table below lists their main features:
Type of Oil | Key Properties |
Naphthenic Oil | Low pour point, boiling point about 425°C, can corrode easier, oxidation products mix in oil. |
Paraffinic Oil | High pour point, boiling point about 530°C, less oxidation, oxidation products do not mix in oil. |
Vegetable oils are also used because they are better for the environment. These oils come from plants and break down faster in nature. They also have a higher ignition point, so they are safer from fire. Checking the oil often, like looking at breakdown voltage and water level, helps keep the oil good and makes the transformer last longer. Clean oil and good insulation help your transformer work safely and well.
Losses and Cooling
No-load and Load Loss
Typical Loss Values and Energy Efficiency
Transformers lose energy in two main ways. No-load loss happens when the transformer is on but not working. Load loss happens when it is giving power to machines. Both losses use up energy in your 35kV Oil-immersed Transformer.
Here is a table with usual loss amounts from IEC 60076 and DOE rules:
Loss Type | Typical Range |
No-Load Losses | 0.2% to 0.3% of rated power |
Load Losses | 0.5% to 1.5% of rated power |
These losses make your transformer less efficient. If losses are low, you save more energy. You also pay less for electricity.
Impact of Losses on Performance and Operating Costs
Losses do more than waste energy. They make the transformer hotter inside. This can make it not last as long. Here are some important things to know:
No-load losses use energy even when not working.
Load losses get bigger when you use more power.
Both losses make your costs go up and efficiency go down.
If you pick a transformer with lower losses, you spend less money. You also help the planet by using less energy.
Cooling Methods
Types of Cooling Systems (ONAN, ONAF, Others)
Cooling stops your transformer from getting too hot. The most used systems are ONAN and ONAF. Here is a table to show how each works:
Cooling Method | Functioning Principle |
Oil-Immersed Self-Cooling (ONAN) | Oil moves on its own and takes heat to the tank. The air cools the tank. No fans or pumps are needed. |
Oil-Immersed Forced-Air Cooling (ONAF) | Fans blow air over the tank and radiators. This cools the transformer faster. It can handle more power. |
Influence of Cooling Methods on Transformer Performance
Good cooling helps your transformer work well and last longer. ONAN systems are quiet and easy to use. ONAF systems cool faster and can handle more power. Things like corrugated tanks and low noise help too. Keep the oil temperature under 85°C. This keeps the transformer safe and working well. Low noise is better for the environment and for people nearby.
Construction and Safety
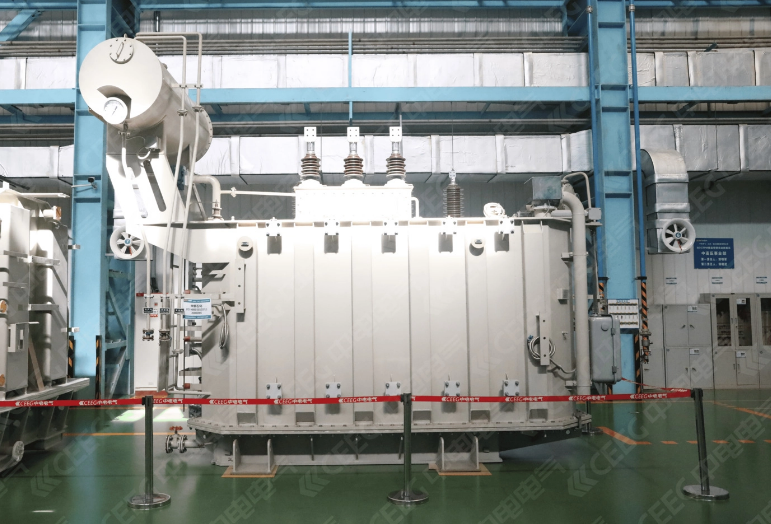

Core and Windings
It is important to know what makes up the core and windings. The core helps guide the magnetic field. The windings carry the electric current. Most 35kV transformers use silicon steel or amorphous metal for the core. Silicon steel is used a lot because it keeps losses low. It also helps save money. Amorphous metal gives even lower core losses. This means the transformer uses energy better.
Windings are usually made from copper or aluminum. Copper lets electricity flow easily. It is also strong. Aluminum is lighter and costs less. But aluminum does not work as well as copper. The table below shows how these materials compare:
Core Material | Magnetic Permeability | Eddy Current Loss | Hysteresis Loss | Typical Application |
Silicon Steel | High | Low | Moderate | Power Transformers |
Amorphous Metal | Very High | Very Low | Low | Energy-Efficient Transformers |
Copper | 5.8 × 10⁷ | 401 | High | High-efficiency transformers |
Aluminum | 3.8 × 10⁷ | 237 | Lower | Cost-sensitive applications |
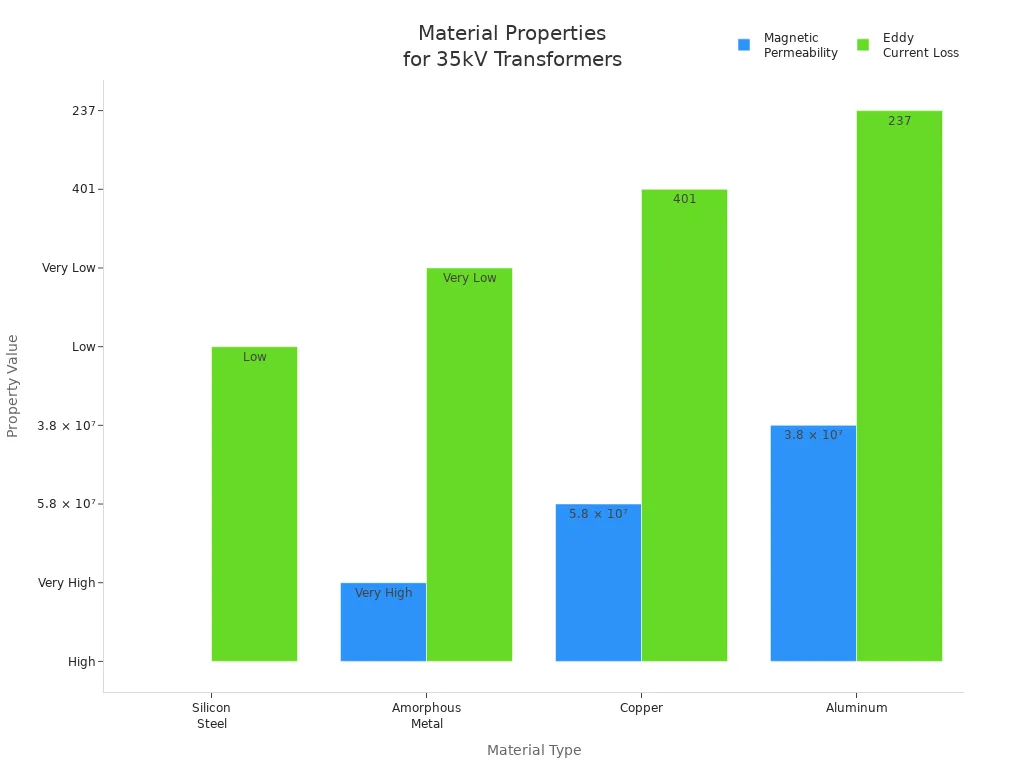
Tip: For the best efficiency, pick copper windings. Amorphous metal cores also help your transformer work better.
Tank and Bushings
The tank keeps the inside parts safe. It also holds the oil. Many tanks are fully sealed. This stops air from getting in. It helps keep the oil good. Corrugated tanks help cool the transformer. They also make the tank stronger. These tanks are safer and simpler than old-style tanks.
Bushings let wires go in and out of the tank. Good bushings stop leaks. They also protect the transformer from damage. Extra safety comes from leak tests and winding checks. Dielectric strength tests are also important. These steps help the transformer handle high voltages.
Fully sealed tanks keep oil from getting old.
Corrugated tanks help with cooling and strength.
Good bushings keep connections safe.
Protection Devices
You want your transformer to be safe. Protection devices help stop fires and oil leaks. They also protect against other dangers. Here are some common systems:
Fire Protection System | Function | Application |
Automatic CO₂ Fire Suppression | Puts out fires without leaving residue | Indoor transformers |
Water Mist Systems | Cools and reduces oil fire intensity | Substations, industrial sites |
Fire Barriers & Blast Walls | Stops fire from spreading | High-risk transformer zones |
Oil Spill Containment Systems | Prevents leaked oil from catching fire | Outdoor transformers |
Modern transformers use smart monitoring systems. These systems watch for heat and gas changes. They can find problems early. This helps you avoid big failures. It keeps your transformer safe and working longer.
Standards and Options
Compliance Standards
You must check if your 35kV oil-immersed transformer follows the right standards. These rules help make sure your equipment is safe and works well. Different places have their own rules. The table below lists the main standards and what they cover:
Standard | Key Requirements |
IEEE C57 Series | General requirements, loading guidance, gas analysis, testing procedures |
IEC 60076 Series | Temperature rise limits, insulation levels, short-circuit strength, sound level measurement |
IEC 60296 | Oil performance criteria, oil testing methods |
GB 1094 Series | Core design, thermal limits, insulation, short-circuit performance |
You should also look for certifications. These prove your transformer meets the rules in each area. Here is a table with common certifications and where they are needed:
Certification | Regions of Compliance |
CE | Europe |
UL | North America |
CSA | North America |
TÜV | Europe |
KEMA | Europe |
ISO | Global |
CEEG knows how to meet these standards and certifications. You can use their transformers for projects in many countries.
Optional Features
You can pick extra features to help your transformer work better for you. Here are some popular choices:
Feature | Description |
Low Oil Consumption | Uses less oil than older tap changers |
Higher Torque Capacity | Handles high voltage jobs with more power |
Reduced Energy Loss | Saves energy and lowers costs |
Reduced Noise | Makes less sound, good for quiet places |
Increased Safety | Has safety features like automatic reset and short circuit protection |
Efficient Operation | Includes thermal and overcurrent protection |
High Durability | Built strong for long life |
Simplified Maintenance | Easy to check and fix, with smart diagnostics |
You can also add:
Easy operation: Change tap settings fast and safely.
Improved efficiency: Helps the transformer work its best.
Reduced maintenance: Needs fewer checks and repairs.
Enhanced safety: Lets you control it from far away.
Some transformers have on-load tap changers. These let you change voltage while the transformer is working. They may also have online oil filters to keep the oil clean and help the transformer last longer. CEEG gives custom solutions, smart monitoring, and green options. You can choose the features that fit your project.
Tip: Picking the right standards and features helps you get a transformer that is safe, works well, and is ready for the future.
When you pick a 35kV oil-immersed transformer, look at important things. Think about load profiles, cooling, safety, and efficiency. High efficiency saves you money on energy. It also helps protect the environment. Always make sure the transformer follows big standards:
Standard | Region | Purpose |
IEC 60076 | Global | General transformer standards |
IEEE C57.12.00 | North America | Performance and safety |
CE | EU | Legal compliance |
Pick suppliers who have lots of experience and certifications. This helps your transformer work well and stay safe for a long time.
FAQ
What is the main job of transformer oil?
Transformer oil cools and insulates your transformer. It stops sparks and helps the transformer last longer. You should check the oil often to keep your transformer safe.
How often should you test transformer oil?
You should test transformer oil at least once a year. Regular testing helps you find problems early. This keeps your transformer working well and prevents damage.
Why do you need to care about insulation class?
Insulation class tells you how much heat your transformer can handle. If you pick the right class, your transformer will work safely and last longer.
What does ONAN mean in transformer cooling?
ONAN stands for Oil Natural Air Natural. Oil moves by itself inside the transformer. Air cools the outside. This method works well for most uses and does not need fans.
Can you use vegetable oil in a 35kV transformer?
Yes, you can use vegetable oil. It is safer for the environment and has a high fire point. Some projects choose vegetable oil for better safety and green benefits.
















